Neuromuscular Plate: What It Is And How It Works
The neuromuscular plate is responsible for the mobilization of the body, through the transmission of information between a motor neuron and the muscles. It is the union that is responsible for transmitting the impulses between the two, which also allows the muscles to contract or relax, depending on what they need.
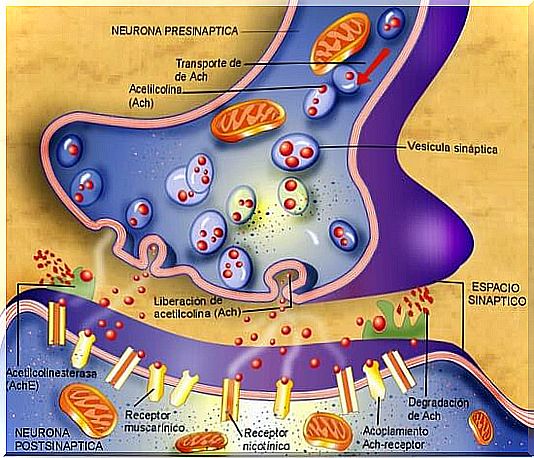
The connection of the neuromuscular plate creates a bridge that occurs between the terminal button of a neuron and the membrane of the muscle fiber. In this way, the neuron’s terminals are connected to the motor end plates, just where nerve impulses are received from a neuromuscular plate.
What are the components of the neuromuscular plate?
The neuromuscular plate is made up of the following elements.
The motor neuron
Also known as a motor neuron, it is a presynaptic neuron that is responsible for emitting nerve impulses that will travel along its axon to the terminal of the muscle.
The main characteristic of this finish is its oval shape that measures approximately 32 microns in width. There are the mitochondria and the postsynaptic membrane. It is where acetylcholine, the main neurotransmitter for muscle stimulation, is created and stored.
The motor neuron is considered to be an alpha motor neuron. This is because it is the cause of the contraction of muscle fibers through the synapse reflected by the release of acetylcholine.
The synaptic cleft
Also called the synaptic space , it is the opening between the motor neuron and the muscle membrane.
Motor plate
It is characterized by being composed of one or more muscle cells that come together to form a muscle fiber. These can be:
- Extrafusal. They are innervated within the neuromuscular plate and are controlled by alpha motor neurons. These direct the force that arises from the contraction of a skeletal muscle.
- Intrafusal. They are responsible for detecting the stretching of the muscle and are parallel to the extrafusal.
Muscle fibers are made up of an enormous number of myofibrils, which in turn are made up of overlapping filaments of actin and myosin.
Actin and myosin are proteins that make up the physiological basis of muscle fibers and are also responsible for muscle contractions.
How does the neuromuscular plate work?
The neuromuscular plates are located within the clefts of the muscle fibers. They work as follows:
- Once an action has been taken, this impulse travels through the motor neuron, releasing acetylcholine.
- When acetylcholine accumulates within the postsynaptic membrane, the endplate potential is produced. This implies the depolarization of the muscular membrane, being this broader compared to any other neuron.
- In depolarization, the channels are opened where the calcium ions will enter.
- Calcium ends up working as a type of cofactor. This helps to extract the energy found in adenosine rifosphate from the cytoplasm of the mitochondria.
- Finally, the potential of the end plate activates the muscle fiber. This causes it to expand through the entire fiber, causing a contraction or jerk.
- A single nerve impulse from a motor neuron causes a contraction in the muscle fiber. In addition, shocks are created much longer than those that have an action potential between two neurons.
- This prolonged jolt is due to the elasticity of the muscle and the time it takes to rid the cells of calcium. However, the more acetylcholine accumulation, the greater the contraction of the muscle fiber.
Neuromuscular plaque diseases
The alteration of the neuromuscular plate is the so-called neuromuscular blockade . This block can occur both presynaptic and post-synaptic, and also in the action of acetylcholyesterase.
The causes of this disorder are usually immune-related or due to drugs or toxins. The main symptoms of neuromuscular blockage are weakness and fatigue.

In addition, there are several specific pathologies that can affect the neuromuscular plate, the terminal button of the motor neuron and the membrane of the muscle fibers. Among the most important and frequent are:
Botulism
Botulism is a condition that causes alteration and inhibition in the acetylcholine release system, the skeletal muscles, and the autonomic nervous system.
This condition is acquired by consuming contaminated food, and produces a very rapid and progressive muscle weakness. Treatments for botulism include induction of vomiting and medications to stimulate bowel movements.
Myasthenia gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a neuromuscular disease that causes inflammation in acetylcholine receptors. For this reason, it produces weakness in the muscles, especially in those that are associated with breathing, salivation and swallowing. A visit to the doctor is necessary for the correct diagnosis and treatment.
Lambert-Eaton syndrome
Lambert-Eaton syndrome is an autoimmune disease. The immune system attacks the calcium pathways of motor neurons. It also generates alterations in the release of acetylcholine. It blocks the spread of the motor action potential, leading to muscle weakness and tumors.
Now that you know the function of this important part of your body, pay attention to the diseases that affect it. If you suspect that you are suffering from any, visit your doctor as soon as possible.