Brain Tumor: Symptoms And Causes
The manifestations of a brain tumor are not very clear, so specific tests are always required to diagnose it. It is a serious health problem that requires immediate action.
A brain tumor is an abnormal growth of cells in the brain tissue. They can be benign, that is, non-cancerous, or malignant, having in their constitution cells of rapid and expansive growth with the possibility of metastasis.
Likewise, they are divided into primary, when they originate in the brain and the neurons found there, and metastatic, if they begin in another part of the body, but reach the brain through metastatic migration.
When the tumor is cancerous, it has a reserved and serious prognosis. It requires specific and meticulous treatments carried out by a medical team that has experience in these approaches. The recovery rate varies depending on the stage of development of the tumor, where it is located, and the general health of the patient.
Possible causes
The reasons for primary brain tumors are unknown. They are known to be preceded by a mutation in DNA that leads abnormal cells to divide uncontrollably and multiply without limit, simultaneously suppressing healthy cells.
What can be mentioned are risk factors, that is, situations or characteristics that are associated with a greater risk of suffering from it. Here we have genetics, heavy metals that poison the nervous system, radiation and diseases such as epilepsy.
In the case of metastatic tumors, the cause is a cancer located elsewhere in the body that migrates cells to the brain. This occurs even if the person is being treated for the original condition.
People who have had colon, breast, lung, or melanoma cancer are the most likely to develop secondary brain tumors. A little because of the way in which these oncological situations evolve, and the same because of the network of vascular and lymphatic vessels that carry circulation between the different tissues.
While there is no sure way to prevent a brain tumor, there is evidence that controlling radiation and environmental toxins reduces the risk. This is key in places where the presence of these agents is high, such as cities, clinics or areas with high voltage power lines.
Signs to watch out for when suspecting a brain tumor
There are certain symptoms that suggest the presence of a brain tumor. It is necessary to clarify that these manifestations, by themselves, are only indicators that must be corroborated through the clinical tests of the case.
Some of the typical symptoms are as follows:
- Headache: if the headache occurs often and is increasing, you should see a doctor. This symptom is an indicator of a brain tumor and occurs in half of those who turn out to be cancer patients. This is because the tumor grows and intracranial pressure increases.
- Nausea and vomiting
- Blurred vision: When there is a brain tumor, blurred vision is usually accompanied by loss of peripheral vision and double vision. Associated hearing difficulties also appear in specific cases.
- Balance problems.
- Fickleness of character or personality.
- Convulsions.
- Excessive drowsiness
Likewise, it is possible that difficulties are experienced in expressing oneself, speaking and even in ordering thoughts or retaining data in memory. Confusion when dealing with specific or everyday topics is a warning.
When a person goes to the medical consultation because they suffer from one or more of the listed symptoms, their primary care professional will order a thorough neurological examination. The initial suspicion is very important and determines the steps to follow in the future.
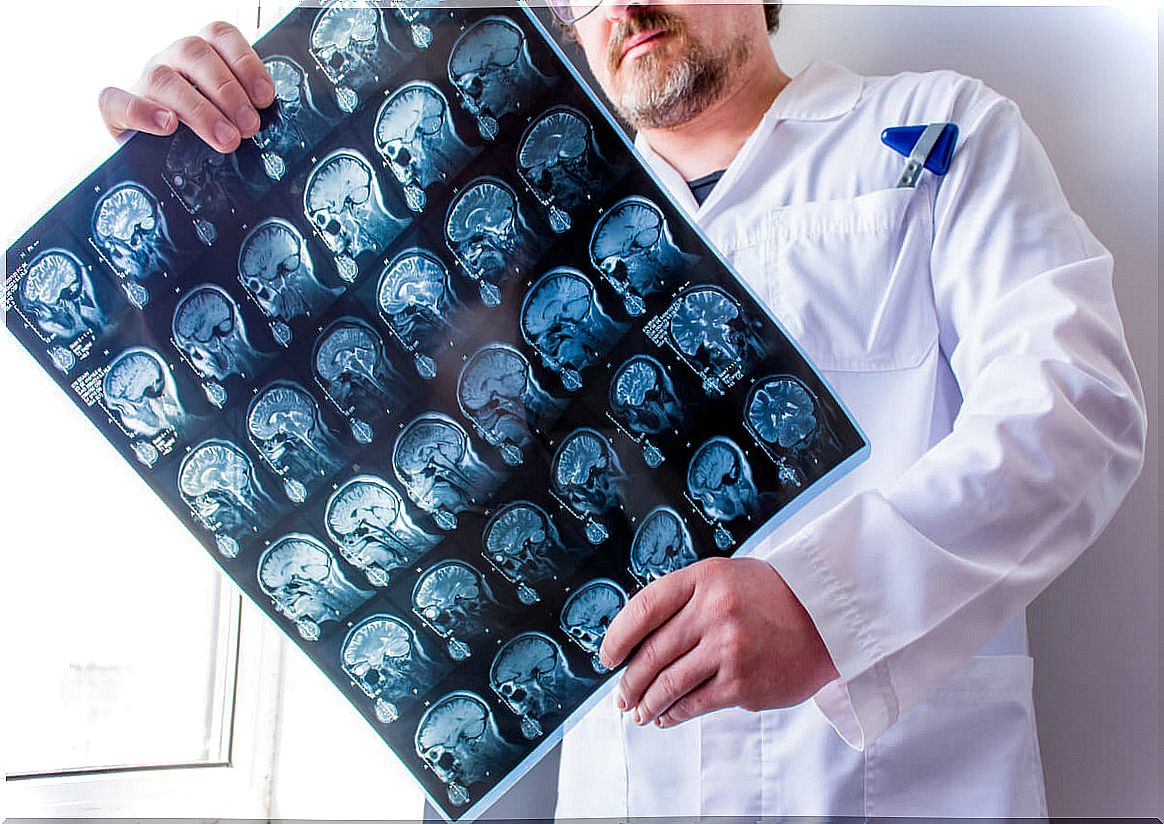
MRIs, CT scans, or even a biopsy may be ordered. The latter, at present, is possible to perform with minimal risks for the patient, since the technique has evolved to make it a more affordable possibility, even considering the delicacy of the brain tissue.

Brain tumor treatment
Once a brain tumor is diagnosed, the treatments are varied and depend on each case. The type of tumor, its location and size are evaluated. In case it is possible to access it and this does not represent a high risk, the usual thing is that surgery is done to remove it.
Surgery can be conventional or performed by radiosurgery. The latter kills tumor cells with radiation and is generally used when the tumor affects a small area.
In some cases, only external radiation therapy is done to destroy the cells. Both surgery and radiation have adverse side effects, such as extreme fatigue, scalp irritation, and amnesia.
Another possibility is chemotherapy. In this case, drugs are given that kill tumor cells, albeit at the cost of more notorious side effects, such as vomiting, nausea, blood disorders, or hair loss.