Quervain’s Tendinitis
This condition is common in people who play sports that involve repetitive wrist movements.

Quervain’s tendinitis or tenosynovitis is a condition that occurs due to irritation of the tendons of the wrist on the thumb side. The irritation causes inflammation in the lining around the tendons, which can make it difficult for them to move.
Those who suffer from it usually feel pain and sensitivity when turning the wrist, making a fist or grasping various elements. Although it can be suffered by men and women, the latter are the most affected, especially when they carry out work or activities that involve repetitive movement of the area.
What are the causes of De Quervain’s tendonitis?

Tendons are fibrous structures that attach muscles to bones. Although it is not known exactly what causes Quervain’s tendonitis, it is hypothesized that it is caused by irritation of the sheath that covers the two tendons of the wrist and the lower part of the thumb.
This, in turn, is related to factors such as:
- Repetitive movements that include the thumb; like typing on the keyboard or using the mouse.
- Microtrauma on the thumb area or the external part of the wrist.
- Tendon degeneration due to age.
- Pathologies such as rheumatoid arthritis.
- Sports involving repetitive hand and wrist movements; like tennis or golf.
Symptoms of De Quervain’s tendonitis
The main symptom of De Quervain’s tendonitis is pain on the thumb side of the wrist. This can manifest itself gradually, although it can also appear abruptly. The pain can radiate to the forearm and tends to be worse when performing activities that strain the hand and thumb.
Symptoms also include:
- Numbness of the thumb and index fingers.
- Swelling of the wrist
- Stiffness when moving the thumb or wrist.
- Hypersensitivity in the wrist and thumb area.
- Difficulty of movement or functional limitation.
How is de Quervain’s tendonitis diagnosed?
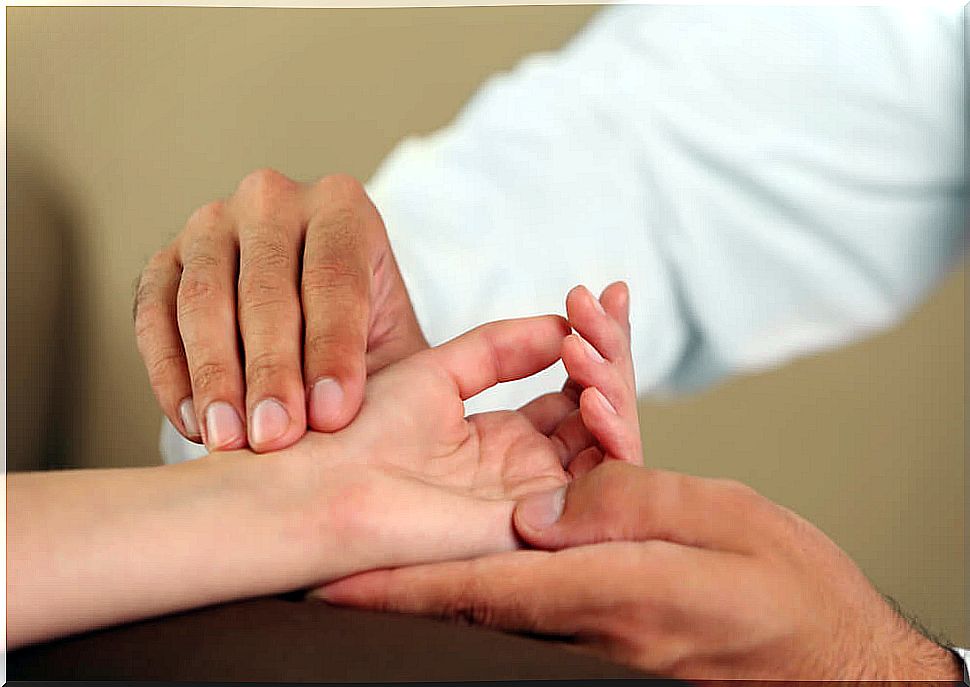
To diagnose de Quervain’s tendonitis, the doctor will examine the hand for pain when applying pressure to the wrist on the thumb side.
After this , a test known as the Finkelstein maneuver is performed. In this, the patient must close the hand by making a fist with the fingers on the thumb. Then flex your wrist toward your little finger to check the intensity of the pain. If this action produces severe pain, the diagnosis suggests de Quervain’s tendonitis.
On the other hand, although it is not necessary, a soft tissue ultrasound can be done to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment of de Quervain’s tendonitis
For successful treatment, the doctor takes into account the severity with which the symptoms occur. At first, a conservative (non-surgical) treatment is used focused on the relief of inflammation and pain. If this does not work, surgical intervention may be suggested.
Medicines
In order to decrease pain and swelling, the doctor suggests consuming over -the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen and naproxen.
Corticosteroid injection into the tendon sheath is also recommended to decrease inflammation. If this treatment is started during the first six months of symptoms, there is a high chance of a full recovery in a short time.
Therapy
To lessen the severity of symptoms and speed up the recovery process, therapy includes:
- Immobilization of the thumb and wrist with a splint or device to support the tendons.
- Avoid repetitive movements with the thumb.
- Apply ice to the affected area.
It is also advisable to visit the physical or occupational therapist. These professionals can evaluate what movements affect the wrist and how to make adjustments to reduce the stress they place on the tendon. Additionally, wrist and hand exercises can be practiced to strengthen muscles and reduce stiffness.
Surgery
The most severe cases do not respond to previous treatments. This is why, as the last route to treatment, outpatient surgery is recommended. This procedure seeks to increase the tunnel space to release tension and facilitate the gliding of the tendon.
Once this intervention is finished, the doctor explains in detail what guidelines must be taken into account for the rehabilitation process. Usually, to avoid future problems, regular visits with the physical therapist are assigned.