Gentamicin: Uses And Side Effects
Gentamicin is an antibiotic that belongs to the aminoglycoside family and is used mainly for the treatment of infections caused by gram-negative bacteria, such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumoniae or Proteus mirabilis .
In addition, it is also active, although to a lesser extent, for the treatment of infections triggered by gram-positive bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus or Enterecoccus faecalis . However, for these types of infections the use of other less toxic drugs is preferred.
It is an antibiotic produced by the microorganism Micromonospora purpurea. Therefore, it is indicated for the management of gastrointestinal, bone, genitourinary, biliary, abdominal and skin infections.
Knowing the history of antibiotics

These widely used drugs, and that so many diseases have been eradicated, were not isolated and identified until the 20th century, which was a great advance in medicine. However, the most remote use of them took place in the Asian country, more than 2,500 years ago.
The first antibiotic discovered was penicillin. The discovery took place in 1897 by Ernest Duchesne, in France. However, his work did not receive the attention of the scientific community. It was later that Alexander Fleming, a British physician, was cultivating Staphylococcus aureus bacteria on an agar plate and it was accidentally contaminated by fungi.
In this way, he noticed that the growing medium around the mold was free of bacteria and reported the discovery in the scientific literature. Since the fungus was of the genus Penicillium , he named it penicillin.
From this discovery, more research began until the discovery of numerous antibiotics that have contributed so much in the field of medicine. Gentamicin was discovered in 1963.
How does gentamicin exert its effect on the body?
Among the aminoglycosides, gentamicin is the most widely used antibiotic. It owes its effectiveness to its ability to inhibit protein synthesis in bacterial cells. To do this, gentamicin has to enter the cell, and it does so through active transport. Then, once inside, in the cytoplasm, it irreversibly binds to the 30S subunit of ribosomes.
In this way, by binding to ribosomes, it succeeds in inhibiting protein synthesis, or makes the proteins that are synthesized defective. Finally, with this inhibition of protein synthesis, it kills the bacteria. That is why it is said to be a bactericidal antibiotic.
Gentamicin administration modes
This antibiotic is, as we have said, active against gram negative bacteria. Due to its low bioavailability, its use is limited to intravenous administration in hospital use. However, it can also be administered intramuscularly in the outpatient setting.
The regimen of administration of these antibiotics is a rapid infusion and in a short space of time so that it does not accumulate and thus reduce adverse reactions.
Adverse reactions
Like all drugs on the market, gentamicin is a drug that is not exempt from producing a series of adverse effects. We understand adverse effects as all those undesirable and unintended events that occur in an expected way with the treatment of a drug.
The most serious adverse reactions are ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity. It is because these structures are similar and gentamicin, like all aminoglycosides, binds to the cell membrane of these tissues and accumulates. Thus, continuous use and at high doses can cause deafness and kidney problems.
Antibiotic resistance
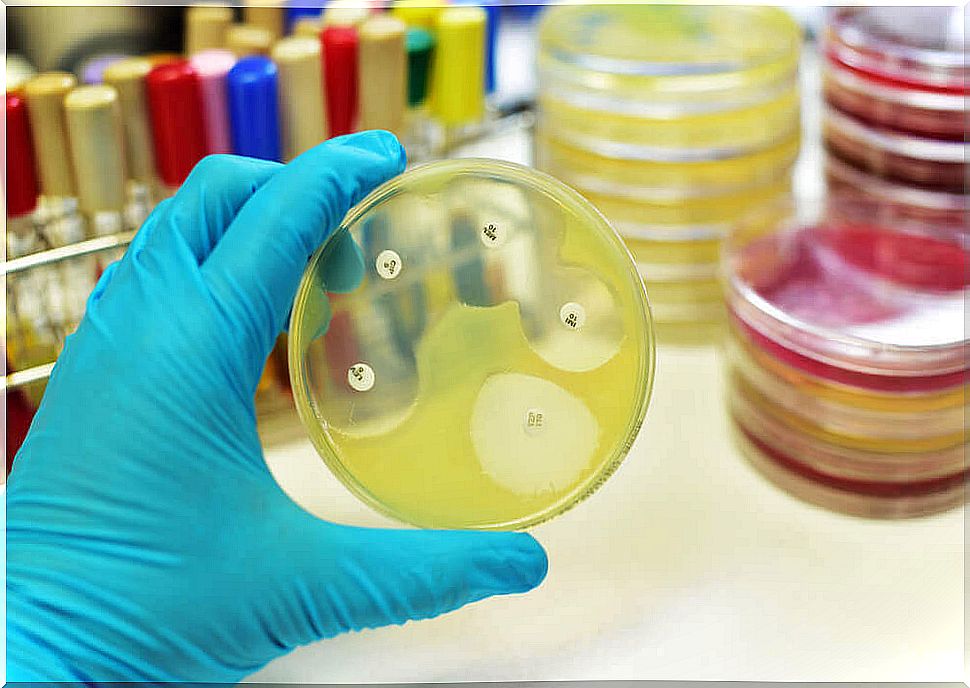
The excessive and inappropriate use of antibiotics accelerates the emergence and spread of resistant bacteria. These microorganisms are capable of developing mechanisms to defend themselves from the ‘attack’ of the drug and thus survive.
In this way, sensitive bacteria are destroyed when exposed to antibiotics, while bacteria that have adopted resistance mechanisms continue to grow and multiply. For this reason, it is extremely important that both health professionals and the general population are aware of the problem and prevent it from worsening in the coming years.
Conclution
Gentamicin is an antibiotic that belongs to the aminoglycoside family. It is used to treat infections caused mainly by gram negative bacteria.
You should never self-medicate with these medications, since improper use favors the appearance of resistance by bacteria. Consequently, the therapeutic arsenal is reduced, reducing the tools to eradicate this type of disease.
Always follow the doctor’s recommendations and consult both with him and with the pharmacist any questions you have about this medicine.