7 Symptoms That Alert You To A Dental Infection
In the event of any worrisome symptoms, we must go to the specialist to rule out or treat a possible dental infection and thus avoid complications. How to recognize a dental infection? Find out!
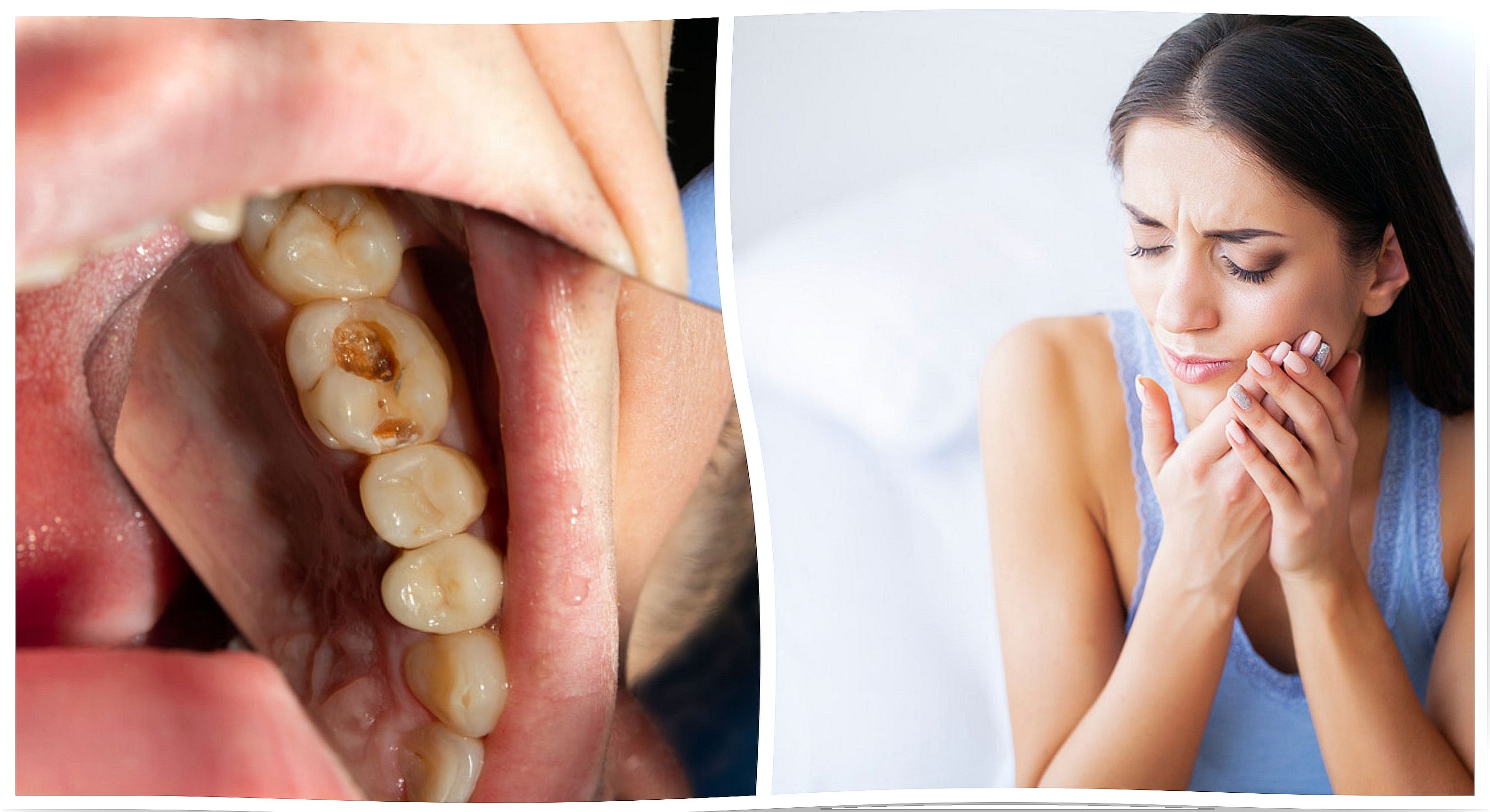
Our teeth are in constant contact with food residues and bacteria. Although the daily practice of oral hygiene helps to keep them clean and healthy, sometimes a dental infection can occur due to factors that escape us.
These infections can be mild or moderate and, in some cases, even compromise the general health of the body. If not treated in time, they can cause very intense pain and the total loss of the affected tooth.
That is why it is essential to know its symptoms and, if you detect them, seek professional help. Pay attention!
1. Bad breath caused by a dental infection
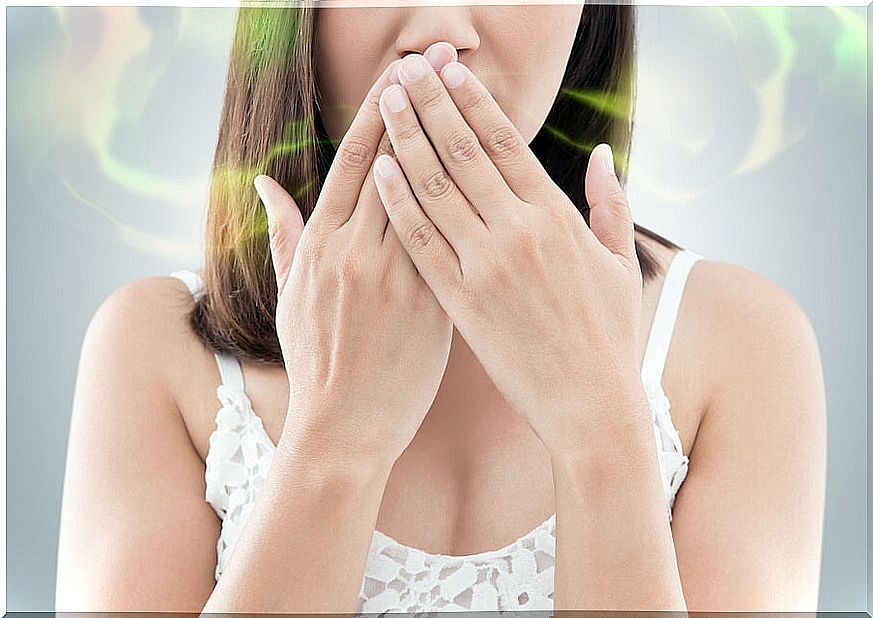

Halitosis is one of the most obvious symptoms of a dental infection, although having bad breath does not imply that there is an infection if there are no other symptoms.
According to a publication in The Journal of Natural Science, Biology and Medicine , bad breath is caused by the excessive proliferation of bacteria, especially in areas where the brush cannot completely eliminate the residue.
If your halitosis is due to an infection, oral hygiene products will only be a temporary solution. Bad breath will reappear until the infection is cleared.
The presence of halitosis could be a sign of:
- Tartar.
- Gingivitis.
- Dental caries.
- Dental abscesses
- Alterations in saliva.
2. Deterioration of tooth enamel
When a dental infection begins to develop, the bacteria on the teeth produce corrosive acids that, over time, affect the enamel that protects them. The foods that increase the presence of these bacteria are fermentable carbohydrates, such as sugar.
The proliferation of acid-producing bacteria occurs in areas where residues from the food we consume accumulate. These areas are easy to identify by their rough texture and yellowish appearance. We can keep that plaque under control with:
- Good hygiene.
- A limited consumption of sugars.
- Letting saliva regulate the pH of the mouth when we are not eating. That means eating less often, or not snacking between meals.
Coinciding with a publication in the National Center for Biotechnology Information , if we do not take care and treat the accumulation of plaque, excess acid can cause a serious weakening of the tooth, causing it to lose density and even break.
3. Pain in the jaw and teeth

In general, infections are related to the accumulation of bacterial plaque. Constant or intermittent pain in the jaw and teeth can alert you to the development of periodontal disease or dental infection. The symptom should be evaluated by a dentist, as it can occur due to different oral conditions or injuries.
4. Bleeding from the gums
Bleeding gums usually appear when there is some type of injury or infection that involves the tissue. It is common to notice them when using the toothbrush or dental floss and, sometimes, when eating some foods.
According to a publication in the National Center for Biotechnology Information , its most common cause is gingivitis, which in turn is caused largely by the growth of bacterial plaque.
5. Swelling and redness
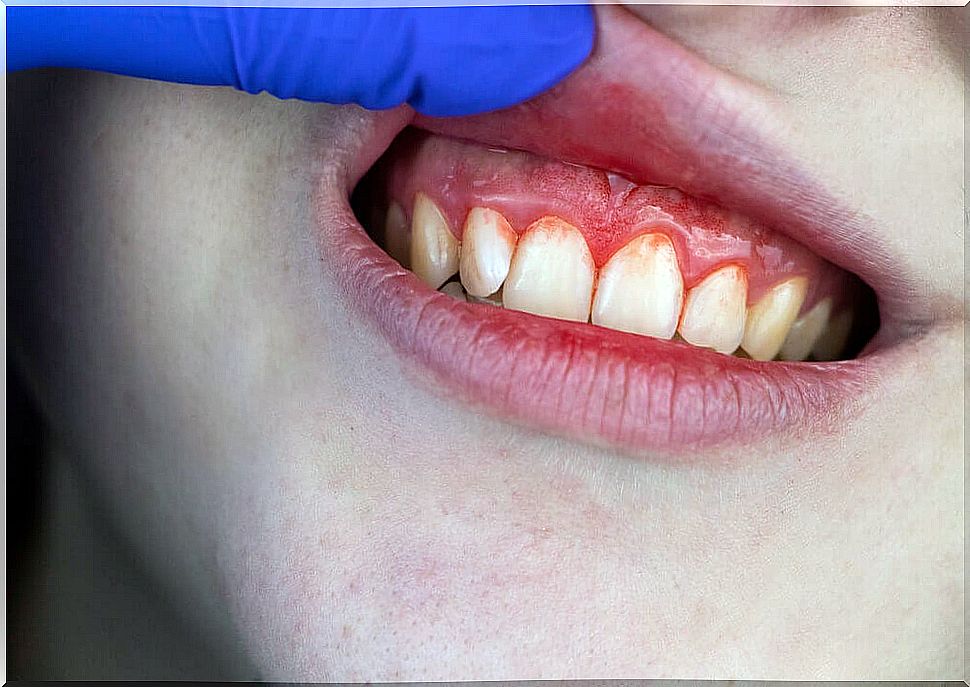
Periodontal infection, and even cavities, causes inflammation and redness in the gums, almost always accompanied by pain. Treating the problem in time is essential to avoid complications. If your gums become swollen, red and painful, see a dentist as soon as possible.
6. Loose teeth
Feeling one of the loose teeth is more than enough reason to consult a dentist as soon as possible, and a symptom of possible periodontitis.
Loose teeth are a sign of the progress of dental infection and, at the same time, alert that the bone structure of the tooth support is eroding. It is common when gingivitis is not controlled in time, which thus becomes periodontitis.
Periodontitis can cause a displacement of the teeth in the affected area and, in more severe cases, causes a deterioration of the bone tissue.
7. Pus
The appearance of pus on the gums is a sign of periodontal disease, and sometimes also of dental infection. The lump of pus or “phlegmon” occurs as a response of the immune system to the attack of the pathogenic bacteria that cause the infection.
- The pus lumps, called abscesses , have blood and pus inside them.
- The abscess is the product of a complex infectious process that must be treated by a professional; If not controlled in time, it can cause irreversible damage.
- The infection can lead to the destruction of alveolar bone (that is, the area of the jaw that supports the teeth) .
Important!
If you suspect that you have a dental infection, see a professional as soon as possible to avoid complications.
Untreated dental abscesses can cause the infection to spread to other areas of the body. It is essential to stop the infection in time with adequate treatment so that this does not happen.
To reduce the risk of dental infections, it is essential to maintain good oral hygiene and, in addition, to consult regularly with the dentist.